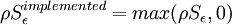Yap correction
From CFD-Wiki
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Where the epsilon equation has been written in the same way is in the CFD-Wiki article on [[low-Re k-epsilon models]]. | Where the epsilon equation has been written in the same way is in the CFD-Wiki article on [[low-Re k-epsilon models]]. | ||
| - | The Yap correction is active in nonequilibrium flows and tends to reduce the departure of the turbulence length scale from its local equilibrium level. | + | The Yap correction is active in nonequilibrium flows and tends to reduce the departure of the turbulence length scale from its local equilibrium level. It is an ad-hoc fix which seldom causes any problems and often improves the predictions. |
| - | Yap showed strongly improved results with the k-epsilon model in separated flows when using this extra source term. | + | Yap showed strongly improved results with the k-epsilon model in separated flows when using this extra source term. The Yep correction has also been shown to improve the results in stagnation region. Launder [[#References|[Launder, B. E. (1993)]]] recommends that the Yap correction should always be used with the epsilon equation. |
==Implementation issues== | ==Implementation issues== | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 25 May 2006
The Yap correction consists of a modifification of the epsilon equation in the form of an extra source term, 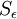 , added to the right hand side of the epsilon equation. The source term can be written as:
, added to the right hand side of the epsilon equation. The source term can be written as:
Where
This source term should be added to the epsilon equation in the following way:
Where the epsilon equation has been written in the same way is in the CFD-Wiki article on low-Re k-epsilon models.
The Yap correction is active in nonequilibrium flows and tends to reduce the departure of the turbulence length scale from its local equilibrium level. It is an ad-hoc fix which seldom causes any problems and often improves the predictions.
Yap showed strongly improved results with the k-epsilon model in separated flows when using this extra source term. The Yep correction has also been shown to improve the results in stagnation region. Launder [Launder, B. E. (1993)] recommends that the Yap correction should always be used with the epsilon equation.
Implementation issues
The Yap source term contains the explicit distance to the nearest wall, 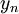 . In an unstructured 3D solver this distance is usually not available and it can be ambiguous how to compute it in more complex topologies. This makes the Yap correction most suitable for use in a structured code where the normal wall distance is readily available.
. In an unstructured 3D solver this distance is usually not available and it can be ambiguous how to compute it in more complex topologies. This makes the Yap correction most suitable for use in a structured code where the normal wall distance is readily available.
When implementing the Yap correction it is common to use it only if the source term is positive. Hence:
References
Launder, B. E. (1993), "Modelling Convective Heat Transfer in Complex Turbulent Flows", Engineering Turbulence Modeling and Experiments 2, Proceedings of the Second International Symposium, Florence, Italy, 31 May - 2 June 1993, Edited by W. Rodi and F. Martelli, Elsevier, 1993, ISBN 0444898026.
Yap, C. J. (1987), Turbulent Heat and Momentum Transfer in Recirculating and Impinging Flows, PhD Thesis, Faculty of Technology, University of Manchester, United Kingdom.

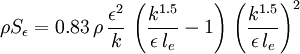
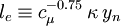
![\frac{\partial}{\partial t} \left( \rho \epsilon \right) +
\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}
\left[
\rho \epsilon u_j - \left( \mu + \frac{\mu_t}{\sigma_\epsilon} \right)
\frac{\partial \epsilon}{\partial x_j}
\right]
=
\left( C_{\epsilon_1} f_1 P - C_{\epsilon_2} f_2 \rho \epsilon \right)
\frac{\epsilon}{k}
+ \rho E
+ \rho S_\epsilon](/W/images/math/a/7/5/a758d253c1fa5a752e369768c8bacac5.png)