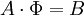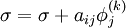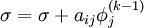Successive over-relaxation method - SOR
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(fixed dot product notation) |
(towards a uniform notation for linear systems : A*Phi = B) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
We seek the solution to set of linear equations: <br> | We seek the solution to set of linear equations: <br> | ||
| - | :<math> A \cdot | + | :<math> A \cdot \Phi = B </math> <br> |
| - | |||
In matrix terms, the definition of the SOR method can be expressed as : <br> | In matrix terms, the definition of the SOR method can be expressed as : <br> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | \phi^{(k)} = \left( {D - \omega L} \right)^{ - 1} \left( {\omega U + \left( {1 - \omega } \right)D} \right)\phi^{(k - 1)} + \omega \left( {D - \omega L} \right)^{ - 1} B | |
</math><br> | </math><br> | ||
Where '''D''','''L''' and '''U''' represent the diagonal, lower triangular and upper triangular matrices of coefficient matrix '''A''' and k is iteration counter.<br> | Where '''D''','''L''' and '''U''' represent the diagonal, lower triangular and upper triangular matrices of coefficient matrix '''A''' and k is iteration counter.<br> | ||
| - | <math> \omega </math> is | + | <math> \omega </math> is a relaxation factor. <br> |
The pseudocode for the SOR algorithm: <br> | The pseudocode for the SOR algorithm: <br> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
=== Algorithm === | === Algorithm === | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | : Chose an intital guess <math> | + | : Chose an intital guess <math>\Phi^{0}</math> to the solution <br> |
: for k := 1 step 1 untill convergence do <br> | : for k := 1 step 1 untill convergence do <br> | ||
:: for i := 1 step until n do <br> | :: for i := 1 step until n do <br> | ||
::: <math> \sigma = 0 </math> <br> | ::: <math> \sigma = 0 </math> <br> | ||
::: for j := 1 step until i-1 do <br> | ::: for j := 1 step until i-1 do <br> | ||
| - | :::: <math> \sigma = \sigma + a_{ij} | + | :::: <math> \sigma = \sigma + a_{ij} \phi_j^{(k)} </math> |
::: end (j-loop) <br> | ::: end (j-loop) <br> | ||
::: for j := i+1 step until n do <br> | ::: for j := i+1 step until n do <br> | ||
| - | :::: <math> \sigma = \sigma + a_{ij} | + | :::: <math> \sigma = \sigma + a_{ij} \phi_j^{(k-1)} </math> |
::: end (j-loop) <br> | ::: end (j-loop) <br> | ||
| - | ::: <math> \sigma = {{\left( { | + | ::: <math> \sigma = {{\left( {b_i - \sigma } \right)} \over {a_{ii} }} </math> |
| - | ::: <math> | + | ::: <math> \phi_i^{(k)} = \phi_i^{(k - 1)} + \omega \left( {\sigma - \phi_i^{k - 1} } \right) </math> |
:: end (i-loop) | :: end (i-loop) | ||
:: check if convergence is reached | :: check if convergence is reached | ||
Revision as of 20:49, 15 December 2005
We seek the solution to set of linear equations:
In matrix terms, the definition of the SOR method can be expressed as :
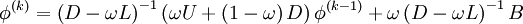
Where D,L and U represent the diagonal, lower triangular and upper triangular matrices of coefficient matrix A and k is iteration counter.
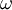 is a relaxation factor.
is a relaxation factor.
The pseudocode for the SOR algorithm:
Algorithm
- Chose an intital guess
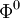 to the solution
to the solution
- for k := 1 step 1 untill convergence do
- for i := 1 step until n do
-
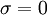
- for j := 1 step until i-1 do
-
- end (j-loop)
- for j := i+1 step until n do
-
- end (j-loop)
-
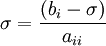
-
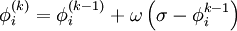
-
- end (i-loop)
- check if convergence is reached
- for i := 1 step until n do
- end (k-loop)
Return to Numerical Methods