Rahman-Siikonen-Agarwal Model
From CFD-Wiki
Introduction
The Rahman-Agarwal-Siikonen (RAS) Turbulence model is a one-equation eddy viscosity model based on 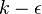 closure. The R-transport equation along with the Bradshaw and other empirical relations are used to solve for the turbulent viscosity. A damping function,
closure. The R-transport equation along with the Bradshaw and other empirical relations are used to solve for the turbulent viscosity. A damping function, 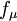 , is used to represent the kinematic blocking by the wall. To avoid defining a wall distance, a Helmholtz-type elliptic relaxation equation is used for
, is used to represent the kinematic blocking by the wall. To avoid defining a wall distance, a Helmholtz-type elliptic relaxation equation is used for 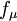 . The model has been validated against a few well-documented flow cases, yielding predictions in good agreement with DNS and experimental data.
. The model has been validated against a few well-documented flow cases, yielding predictions in good agreement with DNS and experimental data.
RAS Model
The turbulent eddy viscosity is given by
The R-transport equation is

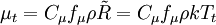
![\begin{matrix}
\frac{\partial \rho R}{\partial t} + \frac{\partial \rho u_j R}{\partial x_j} & = & \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} [ (\mu +\frac{\mu_t}{\sigma})\frac{\partial R}{\partial x_j} ] +C_1 \rho \sqrt{P \tilde{R}} - C_2 \rho (\frac{\partial \tilde{R}}{\partial x_k})^2
\end{matrix}](/W/images/math/c/7/3/c73fd7c551f05ef00f893b25b0725551.png)