A roughness-dependent model
From CFD-Wiki
(→Algebraic eddy viscosity model) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
* {{reference-paper|author=Absi, R. |year=2006|title=[http://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jscejb/62/4/62_437/_article A roughness and time dependent mixing length equation]|rest=Journal of Hydraulic, Coastal and Environmental Engineering, Japan Society of Civil Engineers, (Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshuu B), Vol. 62, No. 4, pp.437-446}} | * {{reference-paper|author=Absi, R. |year=2006|title=[http://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jscejb/62/4/62_437/_article A roughness and time dependent mixing length equation]|rest=Journal of Hydraulic, Coastal and Environmental Engineering, Japan Society of Civil Engineers, (Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshuu B), Vol. 62, No. 4, pp.437-446}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | * {{reference-paper|author=Nezu, I. and Nakagawa, H. |year=1993|title=Turbulence in open-channel flows|rest=A.A. Balkema, Ed. Rotterdam, The Netherlands}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | * {{reference-paper|author=Sukhodolov A., Thiele M. and Bungartz H. |year=1998|title=Turbulence structure in a river reach with sand bed|rest=Water Resour. Res., 34, pp. 1317-1334}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Turbulence models]] | [[Category:Turbulence models]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 21 June 2007
Contents |
Two-equation 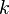 -
- eddy viscosity model
eddy viscosity model
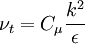 | (1) |
where:
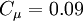
One-equation eddy viscosity model
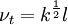 | (2) |
Algebraic eddy viscosity model
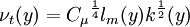 | (3) |
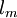 is the mixing length.
is the mixing length.
Algebraic model for the turbulent kinetic energy
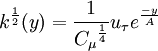 | (4) |
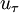 is the shear velocity and
is the shear velocity and 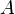 a model parameter.
a model parameter.
For steady open channel flows in local equilibrium, where the energy production is balanced by the dissipation, from the modeled k-equation [Nezu and Nakagawa (1993)] obtained a similar semi-theoretical equation.
Algebraic model for the mixing length
For local equilibrium, an extension of von Kármán’s similarity hypothesis allows to write, with equation (4) [Absi (2006)]:
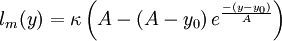 | (5) |
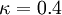 ,
, 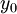 is the hydrodynamic roughness.
For a smooth wall (
is the hydrodynamic roughness.
For a smooth wall (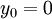 ):
):
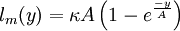 | (6) |
the algebraic eddy viscosity model is therefore
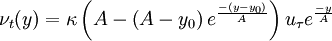 | (7) |
The mean velocity profile
In local equilibrium region, we are able to find the mean velocity profile from the mixing length 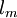 and the turbulent kinetic energy
and the turbulent kinetic energy 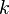 by:
by:
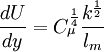 | (8) |
With equations (4) and (5), we obtain:
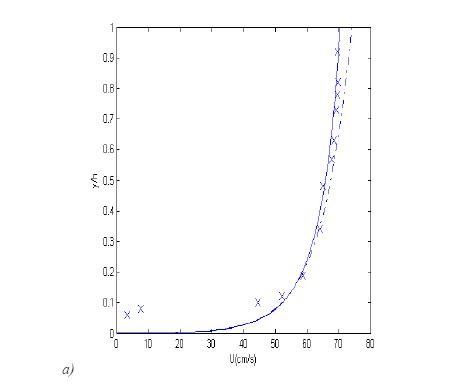
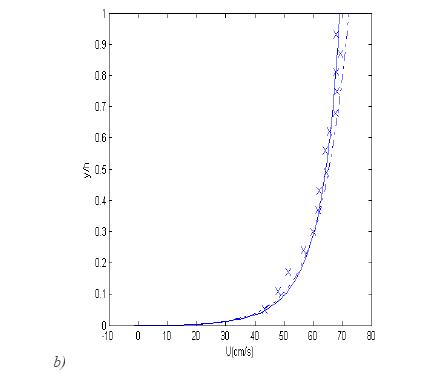
Fig. Vertical distribution of mean flow velocity.
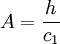 ;
; 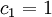 ;
Dash-dotted line: logarithmic profile; solid line: obtained from equation (8); symbols: experimental data (Sukhodolov et al). a) profile 2:
;
Dash-dotted line: logarithmic profile; solid line: obtained from equation (8); symbols: experimental data (Sukhodolov et al). a) profile 2: 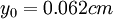 ;
; 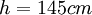 ;
; 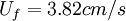 . b) profile 4:
. b) profile 4: 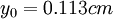 ;
; 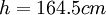 ;
; 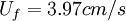 ; values of
; values of 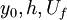 are from [Sukhodolov et al. (1998)].
are from [Sukhodolov et al. (1998)].
References
- Absi, R. (2006), "A roughness and time dependent mixing length equation", Journal of Hydraulic, Coastal and Environmental Engineering, Japan Society of Civil Engineers, (Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshuu B), Vol. 62, No. 4, pp.437-446.
- Nezu, I. and Nakagawa, H. (1993), "Turbulence in open-channel flows", A.A. Balkema, Ed. Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- Sukhodolov A., Thiele M. and Bungartz H. (1998), "Turbulence structure in a river reach with sand bed", Water Resour. Res., 34, pp. 1317-1334.