 |
|
|
[Sponsors] | |||||
|
|
|
#1 |
|
New Member
kalyan
Join Date: Oct 2010
Posts: 19
Rep Power: 16  |
I do have a .stl file of a ventilator design to be fit into a rectangular box of certain dimensions.
So for meshing the box and the ventilator fan together am using snappyHexMesh. The rectangular box is created as a base design with inlet,outlet and walls in blockmeshdict file. The .stl files of the ventilator are placed in the trisurface folder of constant. The meshing process worked fine and i have a mesh. To work with the MRFSimpleFoam i need to use the cellSet and faceSet. But, to my disappointment the cellZones and faceZones files in the polyMesh are empty. So am unable to use the cellset and faceset commands as there are no zones available. The snappyHexMeshDict file is as follows castellatedMesh true; // true; snap true; // true; addLayers false; // true; // Geometry. Definition of all surfaces. All surfaces are of class // searchableSurface. // Surfaces are used // - to specify refinement for any mesh cell intersecting it // - to specify refinement for any mesh cell inside/outside/near // - to 'snap' the mesh boundary to the surface geometry { mod2.stl { type triSurfaceMesh; name fan; } modh.stl { type triSurfaceMesh; name holder; } air //the dimensions used for the base design in blockmesh dict file are same { type searchableBox; min (-1.18591 -0.489586 -0.103673); max (-0.382905 0.290414 0.468327); } }; // Settings for the castellatedMesh generation. castellatedMeshControls { // Refinement parameters // ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ // While refining maximum number of cells per processor. This is basically // the number of cells that fit on a processor. If you choose this too small // it will do just more refinement iterations to obtain a similar mesh. maxLocalCells 1000000; // Overall cell limit (approximately). Refinement will stop immediately // upon reaching this number so a refinement level might not complete. // Note that this is the number of cells before removing the part which // is not 'visible' from the keepPoint. The final number of cells might // actually be a lot less. maxGlobalCells 2000000; // The surface refinement loop might spend lots of iterations refining just a // few cells. This setting will cause refinement to stop if <= minimumRefine // are selected for refinement. Note: it will at least do one iteration // (unless the number of cells to refine is 0) minRefinementCells 10; // Number of buffer layers between different levels. // 1 means normal 2:1 refinement restriction, larger means slower // refinement. nCellsBetweenLevels 3; // 2; // Explicit feature edge refinement // ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ // Specifies a level for any cell intersected by its edges. // This is a featureEdgeMesh, read from constant/triSurface for now. features ( //{ // file "someLine.eMesh"; // level 2; //} ); // Surface based refinement // ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ // Specifies two levels for every surface. The first is the minimum level, // every cell intersecting a surface gets refined up to the minimum level. // The second level is the maximum level. Cells that 'see' multiple // intersections where the intersections make an // angle > resolveFeatureAngle get refined up to the maximum level. refinementSurfaces { fan { // Surface-wise min and max refinement level level (3 4); // 5 6 } holder { // Surface-wise min and max refinement level level (3 4); // 5 6 } } // Resolve sharp angles resolveFeatureAngle 30.0; // 30; // Region-wise refinement // ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ // Specifies refinement level for cells in relation to a surface. One of // three modes // - distance. 'levels' specifies per distance to the surface the // wanted refinement level. The distances need to be specified in // descending order. // - inside. 'levels' is only one entry and only the level is used. All // cells inside the surface get refined up to the level. The surface // needs to be closed for this to be possible. // - outside. Same but cells outside. refinementRegions { air { mode inside; // inside; levels ((1E15 4)); //1E15 4 } } // Mesh selection // ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ // After refinement patches get added for all refinementSurfaces and // all cells intersecting the surfaces get put into these patches. The // section reachable from the locationInMesh is kept. // NOTE: This point should never be on a face, always inside a cell, even // after refinement. locationInMesh (-0.6509053 -0.0995863 0.182327); } // Settings for the snapping. snapControls { //- Number of patch smoothing iterations before finding correspondence // to surface nSmoothPatch 3; //- Relative distance for points to be attracted by surface feature point // or edge. True distance is this factor times local // maximum edge length. tolerance 4.0; //- Number of mesh displacement relaxation iterations. nSolveIter 30; //- Maximum number of snapping relaxation iterations. Should stop // before upon reaching a correct mesh. nRelaxIter 5; } // Settings for the layer addition. addLayersControls { relativeSizes true; //true; // v 1.6 // Per final patch (so not geometry!) the layer information layers { //minZ //{ // nSurfaceLayers 3; //} stlSurface_fan // a_surface_name { nSurfaceLayers 5; } } // Expansion factor for layer mesh expansionRatio 1.4; // 1.0; //- Wanted thickness of final added cell layer. If multiple layers // is the // thickness of the layer furthest away from the wall. // Relative to undistorted size of cell outside layer. //finalLayerRatio FINALLAYERRATIO; // 0.3; finalLayerThickness 0.6; // 0.3; // v 1.6 //- Minimum thickness of cell layer. If for any reason layer // cannot be above minThickness do not add layer. // Relative to undistorted size of cell outside layer. minThickness 0.001; // 0.1; //- If points get not extruded do nGrow layers of connected faces that are // also not grown. This helps convergence of the layer addition process // close to features. nGrow 1; // 1; // Advanced settings //- When not to extrude surface. 0 is flat surface, 90 is when two faces // make straight angle. featureAngle 179; // 30; //- Maximum number of snapping relaxation iterations. Should stop // before upon reaching a correct mesh. nRelaxIter 3; // Number of smoothing iterations of surface normals nSmoothSurfaceNormals 1; // Number of smoothing iterations of interior mesh movement direction nSmoothNormals 3; // Smooth layer thickness over surface patches nSmoothThickness 10; // Stop layer growth on highly warped cells maxFaceThicknessRatio 0.5; // Reduce layer growth where ratio thickness to medial // distance is large maxThicknessToMedialRatio 0.3; // Angle used to pick up medial axis points minMedianAxisAngle 130; // Create buffer region for new layer terminations nBufferCellsNoExtrude 0; // Overall max number of layer addition iterations // v 1.6 nLayerIter 50; // v 1.6 } // Generic mesh quality settings. At any undoable phase these determine // where to undo. meshQualityControls { //- Maximum non-orthogonality allowed. Set to 180 to disable. maxNonOrtho 65; //- Max skewness allowed. Set to <0 to disable. maxBoundarySkewness 20; maxInternalSkewness 4; //- Max concaveness allowed. Is angle (in degrees) below which concavity // is allowed. 0 is straight face, <0 would be convex face. // Set to 180 to disable. maxConcave 80; //- Minimum projected area v.s. actual area. Set to -1 to disable. minFlatness 0.5; //- Minimum pyramid volume. Is absolute volume of cell pyramid. // Set to very negative number (e.g. -1E30) to disable. minVol 1e-13; //- Minimum face area. Set to <0 to disable. minArea -1; //- Minimum face twist. Set to <-1 to disable. dot product of face normal //- and face centre triangles normal minTwist 0.02; //- minimum normalised cell determinant //- 1 = hex, <= 0 = folded or flattened illegal cell minDeterminant 0.001; //- minFaceWeight (0 -> 0.5) minFaceWeight 0.02; //- minVolRatio (0 -> 1) minVolRatio 0.01; //must be >0 for Fluent compatibility minTriangleTwist -1; // Advanced //- Number of error distribution iterations nSmoothScale 4; //- amount to scale back displacement at error points errorReduction 0.75; } // Advanced // Flags for optional output // 0 : only write final meshes // 1 : write intermediate meshes // 2 : write volScalarField with cellLevel for postprocessing // 4 : write current intersections as .obj files debug 0; // Merge tolerance. Is fraction of overall bounding box of initial mesh. // Note: the write tolerance needs to be higher than this. mergeTolerance 1E-6; // ************************************************** *********************** // The design of the ventilator with the rectangular box is 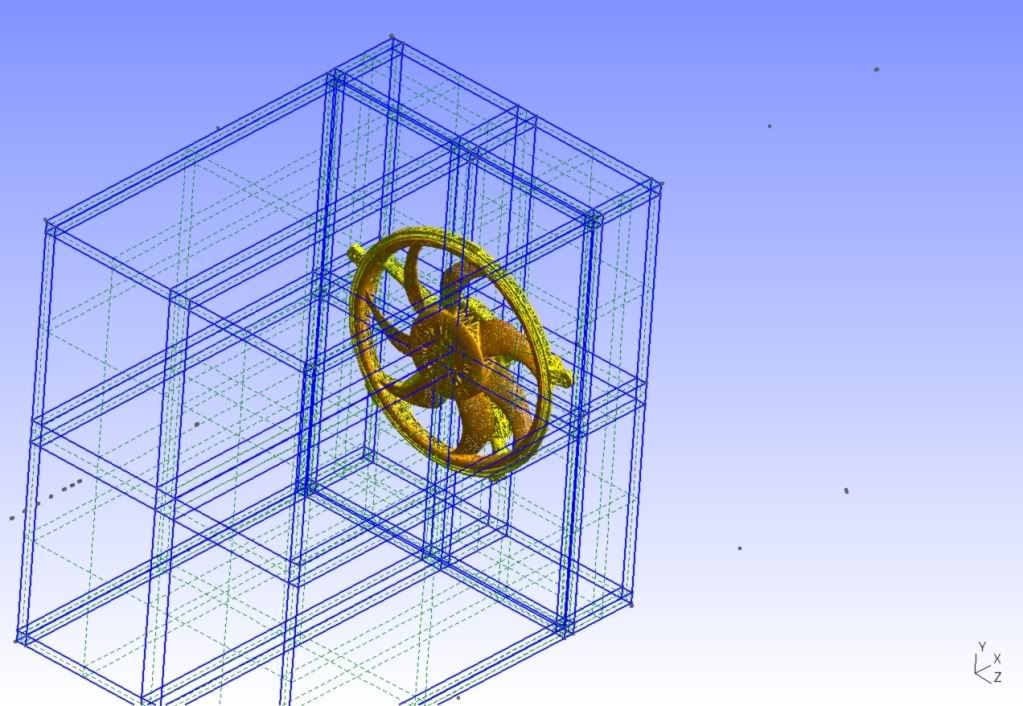 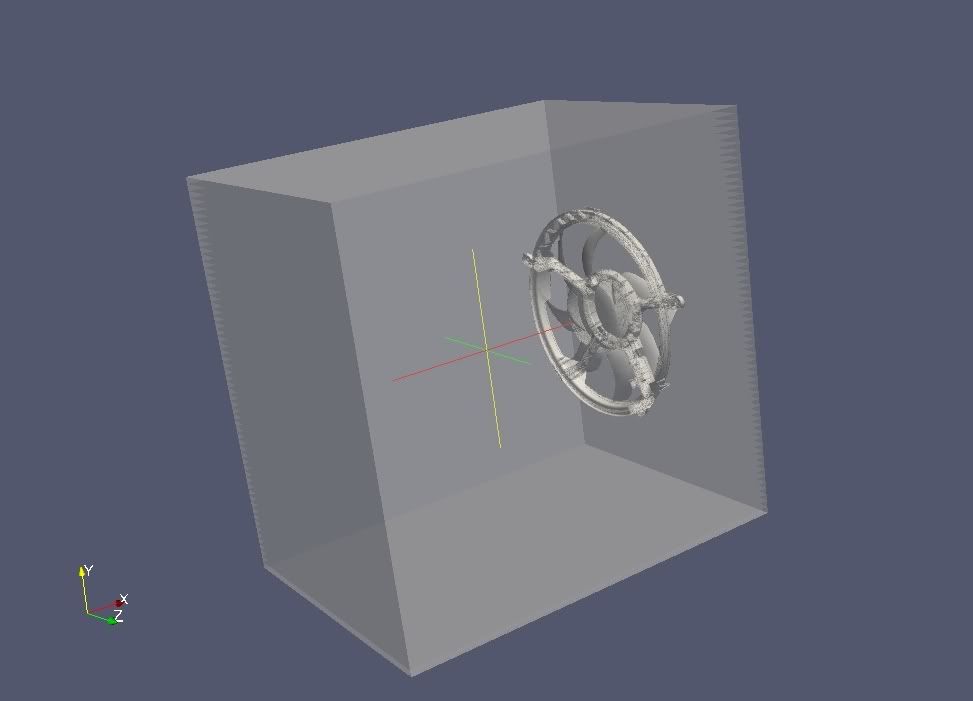
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
#2 |
|
New Member
kalyan
Join Date: Oct 2010
Posts: 19
Rep Power: 16  |
How to set the cell zones and face zones in order to work with the commands cellSet and faceSet for the MRFSimpleFoam solver?

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
#3 |
|
Member
Jean-Michel FONTAINE
Join Date: Aug 2009
Location: Orleans - France
Posts: 55
Rep Power: 17  |
Hi hardykalyan
You may have to create a file system/cellSetDict containing something like : name rotor; action new; topoSetSources ( cylinderToCell { p1 (-12005 0 0); // start point on axis p2 (12005 0 0); // end point on axis radius 34885; } ); See useful cellSetDict samples in OpenFOAM-x.x/applications/utilities/mesh/manipulation/ cellSet Best wishes J-Michel |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
#4 |
|
New Member
|
Try this out....
See if it help !!!!!! http://www.cfd-online.com/Forums/blo...pyhexmesh.html Regards, Amol |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
#5 |
|
New Member
kalyan
Join Date: Oct 2010
Posts: 19
Rep Power: 16  |
I don't know if the cylinder option either in cellSetDict/snappyHexMeshDict will also include the air region between the wings. I will try both of the cases and shall let you know soon.
Thank you once again for your response 
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
#6 | |
|
New Member
kalyan
Join Date: Oct 2010
Posts: 19
Rep Power: 16  |
Quote:
I have tried using the cylinderToCell and I am really confused with this. If i use cylinderToCell to include the ventilator in it, does it also include the air regions between the wings of the ventilator? And also in the figures i provided there is a hanger around the fan with some hinges at some edges and so should I use boxToCell for the hanger? Thanking you in advance.... |
||
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
#7 |
|
Senior Member
Vincent RIVOLA
Join Date: Mar 2009
Location: France
Posts: 283
Rep Power: 18  |
did you manage to solve your problem.
I am trying to simulate something close to this. |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
#8 |
|
Senior Member
|
Hi,
I managed to use snappyHexMesh to obtain a mesh for MRFSimpleFoam. My case study is a stirred tank reactor, where I need an inner cylinder that encloses the propeller to rotate. It worked for me including the following in snappyHexMeshDict: geometry { cylinder { type searchableCylinder; point1 (0 0 100); point2 (0 0 3000); radius 650; name cylinder; } . . . } refinementSurfaces { cylinder { level (1 1); regions {} faceZone MRF; //name of faceZone cellZone MRF; // name of cellZone zoneInside true; // to include all cells inside the enclosed cylinder } . . . } Regards, Jose |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
#9 |
|
New Member
kalyan
Join Date: Oct 2010
Posts: 19
Rep Power: 16  |
I have finished my project with success.. I experimented cutting the region of the fan from the box and failed and so have performed with the selection of cylindrical region where I have obtained some good results.
Thank you for all the support to all members who offered me help 
|
|
|
|

|
|
 |
|
|