 April 24, 2016, 12:25
April 24, 2016, 12:25
|
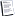 Meshing connections of round and straight edges
Meshing connections of round and straight edges
|
#1
|
|
New Member
Jonathan
Join Date: Apr 2016
Posts: 3
Rep Power: 10
|
Hi everyone,
I'm running into problems when I try to do the meshing at the centre of a rotor where the blades connect. The mesh that gets build has errors like holes and intersecting pyramids. These errors are visible in Paraview and my simulation crashes.
I've run a few simulations before, but now I want to work on details close to the centre of the rotor. I'm extending the incompressible/propeller example and I'm using an object built in blender. My blender object also passes the 3D-printing test in blender, so I guess I'm doing something wrong with snappyHexMesh.
Attached is a screenshot with an example. The straight parts of the mesh point upwards by roughly 45°. The straight parts connect to a circualar ring, this ring is also far from being round.
Here's my snappyHexMesh file:
Code:
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 3.0.x |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
object snappyHexMeshDict;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
// Which of the steps to run
castellatedMesh true;
snap true;
addLayers true;
// Geometry. Definition of all surfaces. All surfaces are of class
// searchableSurface.
// Surfaces are used
// - to specify refinement for any mesh cell intersecting it
// - to specify refinement for any mesh cell inside/outside/near
// - to 'snap' the mesh boundary to the surface
geometry
{
innerCylinder.obj
{
type triSurfaceMesh;
name innerCylinder;
regions
{
ascii
{
name innerCylinder;
}
}
}
innerCylinderSmall.obj
{
type triSurfaceMesh;
name innerCylinderSmall;
regions
{
ascii
{
name innerCylinderSmall;
}
}
}
outerCylinder.obj
{
type triSurfaceMesh;
name outerCylinder;
regions
{
ascii
{
name outerCylinder;
}
}
}
propellerTip.obj.gz
{
type triSurfaceMesh;
name propellerTip;
regions
{
ascii
{
name propellerTip;
}
}
}
//propellerStem1.obj
//{
// type triSurfaceMesh;
// name propellerStem1;
// regions
// {
// ascii
// {
// name propellerStem1;
// }
// }
//}
//propellerStem2.obj
//{
// type triSurfaceMesh;
// name propellerStem2;
// regions
// {
// ascii
// {
// name propellerStem2;
// }
// }
//}
//propellerStem3.obj
//{
// type triSurfaceMesh;
// name propellerStem3;
// regions
// {
// ascii
// {
// name propellerStem3;
// }
// }
//}
};
// Settings for the castellatedMesh generation.
castellatedMeshControls
{
// Refinement parameters
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// If local number of cells is >= maxLocalCells on any processor
// switches from from refinement followed by balancing
// (current method) to (weighted) balancing before refinement.
maxLocalCells 100000;
// Overall cell limit (approximately). Refinement will stop immediately
// upon reaching this number so a refinement level might not complete.
// Note that this is the number of cells before removing the part which
// is not 'visible' from the keepPoint. The final number of cells might
// actually be a lot less.
maxGlobalCells 2000000;
// The surface refinement loop might spend lots of iterations refining just a
// few cells. This setting will cause refinement to stop if <= minimumRefine
// are selected for refinement. Note: it will at least do one iteration
// (unless the number of cells to refine is 0)
minRefinementCells 10;
// Allow a certain level of imbalance during refining
// (since balancing is quite expensive)
// Expressed as fraction of perfect balance (= overall number of cells /
// nProcs). 0=balance always.
maxLoadUnbalance 0.10;
// Number of buffer layers between different levels.
// 1 means normal 2:1 refinement restriction, larger means slower
// refinement.
nCellsBetweenLevels 4;
// Explicit feature edge refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies a level for any cell intersected by its edges.
// This is a featureEdgeMesh, read from constant/triSurface for now.
features
(
{
file "innerCylinderSmall.eMesh";
level 4;
}
{
file "outerCylinder.eMesh";
level 0;
}
{
file "propellerTip.eMesh";
level 5;//vorher 4
}
// {
// file "propellerStem1.eMesh";
// level 4;
// }
// {
// file "propellerStem2.eMesh";
// level 4;
// }
// {
// file "propellerStem3.eMesh";
// level 4;
// }
);
// Surface based refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies two levels for every surface. The first is the minimum level,
// every cell intersecting a surface gets refined up to the minimum level.
// The second level is the maximum level. Cells that 'see' multiple
// intersections where the intersections make an
// angle > resolveFeatureAngle get refined up to the maximum level.
refinementSurfaces
{
innerCylinderSmall
{
level (4 4);
faceType boundary;
cellZone innerCylinderSmall;
faceZone innerCylinderSmall;
cellZoneInside inside;
}
outerCylinder
{
level (0 0);
}
propellerTip
{
level (6 7); //vorher (4 5)
}
//propellerStem1
//{
// level (4 4);
//}
//propellerStem2
//{
// level (4 4);
//}
//propellerStem3
//{
// level (4 4);
//}
}
// Resolve sharp angles
resolveFeatureAngle 30;
// Region-wise refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies refinement level for cells in relation to a surface. One of
// three modes
// - distance. 'levels' specifies per distance to the surface the
// wanted refinement level. The distances need to be specified in
// descending order.
// - inside. 'levels' is only one entry and only the level is used. All
// cells inside the surface get refined up to the level. The surface
// needs to be closed for this to be possible.
// - outside. Same but cells outside.
refinementRegions
{
innerCylinder
{
mode inside;
levels ((1E15 3));
}
innerCylinderSmall
{
mode inside;
levels ((1E15 4)); //vorher 4
}
}
// Mesh selection
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// After refinement patches get added for all refinementSurfaces and
// all cells intersecting the surfaces get put into these patches. The
// section reachable from the locationInMesh is kept.
// NOTE: This point should never be on a face, always inside a cell, even
// after refinement.
locationInMesh (0.0 0.0 0.0);
// Whether any faceZones (as specified in the refinementSurfaces)
// are only on the boundary of corresponding cellZones or also allow
// free-standing zone faces. Not used if there are no faceZones.
allowFreeStandingZoneFaces false;
}
// Settings for the snapping.
snapControls
{
//- Number of patch smoothing iterations before finding correspondence
// to surface
nSmoothPatch 3;
//- Relative distance for points to be attracted by surface feature point
// or edge. True distance is this factor times local
// maximum edge length.
tolerance 10.0; // 1.0;
//- Number of mesh displacement relaxation iterations.
nSolveIter 30;
//- Maximum number of snapping relaxation iterations. Should stop
// before upon reaching a correct mesh.
nRelaxIter 5;
// Feature snapping
// Number of feature edge snapping iterations.
// Leave out altogether to disable.
nFeatureSnapIter 10;
// Detect (geometric only) features by sampling the surface
// (default=false).
implicitFeatureSnap true;
// Use castellatedMeshControls::features (default = true)
explicitFeatureSnap false;
// Detect features between multiple surfaces
// (only for explicitFeatureSnap, default = false)
multiRegionFeatureSnap true;
}
// Settings for the layer addition.
addLayersControls
{
// Are the thickness parameters below relative to the undistorted
// size of the refined cell outside layer (true) or absolute sizes (false).
relativeSizes true;
// Per final patch (so not geometry!) the layer information
layers
{
propellerTip
{
nSurfaceLayers 4;
}
}
// Expansion factor for layer mesh
expansionRatio 1.2;
// Wanted thickness of final added cell layer. If multiple layers
// is the thickness of the layer furthest away from the wall.
// Relative to undistorted size of cell outside layer.
// See relativeSizes parameter.
finalLayerThickness 0.3;
// Minimum thickness of cell layer. If for any reason layer
// cannot be above minThickness do not add layer.
// Relative to undistorted size of cell outside layer.
minThickness 0.05;
// If points get not extruded do nGrow layers of connected faces that are
// also not grown. This helps convergence of the layer addition process
// close to features.
// Note: changed(corrected) w.r.t 17x! (didn't do anything in 17x)
nGrow 0;
// Advanced settings
// When not to extrude surface. 0 is flat surface, 90 is when two faces
// are perpendicular
featureAngle 60;
// Maximum number of snapping relaxation iterations. Should stop
// before upon reaching a correct mesh.
nRelaxIter 3;
// Number of smoothing iterations of surface normals
nSmoothSurfaceNormals 1;
// Number of smoothing iterations of interior mesh movement direction
nSmoothNormals 3;
// Smooth layer thickness over surface patches
nSmoothThickness 10;
// Stop layer growth on highly warped cells
maxFaceThicknessRatio 0.5;
// Reduce layer growth where ratio thickness to medial
// distance is large
maxThicknessToMedialRatio 0.3;
// Angle used to pick up medial axis points
// Note: changed(corrected) w.r.t 17x! 90 degrees corresponds to 130 in 17x.
minMedianAxisAngle 90;
// Create buffer region for new layer terminations
nBufferCellsNoExtrude 0;
// Overall max number of layer addition iterations. The mesher will exit
// if it reaches this number of iterations; possibly with an illegal
// mesh.
nLayerIter 50;
}
// Generic mesh quality settings. At any undoable phase these determine
// where to undo.
meshQualityControls
{
//- Maximum non-orthogonality allowed. Set to 180 to disable.
maxNonOrtho 65;
//- Max skewness allowed. Set to <0 to disable.
maxBoundarySkewness 20;
maxInternalSkewness 4;
//- Max concaveness allowed. Is angle (in degrees) below which concavity
// is allowed. 0 is straight face, <0 would be convex face.
// Set to 180 to disable.
maxConcave 80;
//- Minimum pyramid volume. Is absolute volume of cell pyramid.
// Set to a sensible fraction of the smallest cell volume expected.
// Set to very negative number (e.g. -1E30) to disable.
minVol 1e-13;
//- Minimum quality of the tet formed by the face-centre
// and variable base point minimum decomposition triangles and
// the cell centre. This has to be a positive number for tracking
// to work. Set to very negative number (e.g. -1E30) to
// disable.
// <0 = inside out tet,
// 0 = flat tet
// 1 = regular tet
minTetQuality -1; // 1e-30;
//- Minimum face area. Set to <0 to disable.
minArea -1;
//- Minimum face twist. Set to <-1 to disable. dot product of face normal
// and face centre triangles normal
minTwist 0.01;
//- Minimum normalised cell determinant
// 1 = hex, <= 0 = folded or flattened illegal cell
minDeterminant 0.001;
//- minFaceWeight (0 -> 0.5)
minFaceWeight 0.05;
//- minVolRatio (0 -> 1)
minVolRatio 0.01;
//must be >0 for Fluent compatibility
minTriangleTwist -1;
// Advanced
//- Number of error distribution iterations
nSmoothScale 4;
//- Amount to scale back displacement at error points
errorReduction 0.75;
// Optional : some meshing phases allow usage of relaxed rules.
// See e.g. addLayersControls::nRelaxedIter.
relaxed
{
//- Maximum non-orthogonality allowed. Set to 180 to disable.
maxNonOrtho 75;//vorher: 75
}
}
// Merge tolerance. Is fraction of overall bounding box of initial mesh.
// Note: the write tolerance needs to be higher than this.
mergeTolerance 1e-6; //vorher 1e-6
// ************************************************************************* //
I'm glad to finally join the forum, google has often brought me here and you've been great help already!
|

|

|





 Similar Threads
Similar Threads