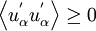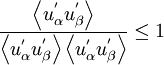Realisability and Schwarz' inequality
From CFD-Wiki
Realisability is the minimum requirement to prevent a turbulence model generating non-physical results. For a model to be realisable the normal Reynolds stresses must be non-negative and the Schwarz' inequality must be satisfied between fluctuating quantities:
where there is no summation over the indices. Some workers only apply the first inequality to satisfy realisability, or maintain non-negative vales of k and epsilon. This "weak" form of realisability is satisfied in non-linear models by setting 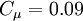 .
.
References
Speziale, C.G. (1991), "Analytical methods for the development of Reynolds-stress closures in turbulence", Ann. Rev. Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 23, pp107-157.